By Alec MacGillis, ProPublica
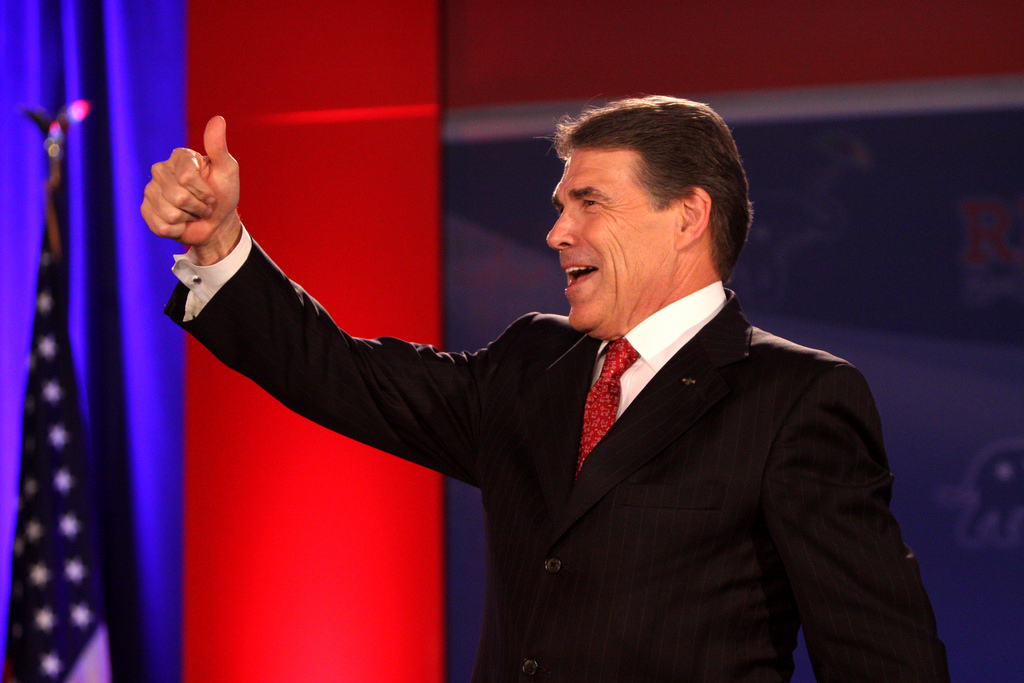
Donald Trump’s selection of Rick Perry to lead the Department of Energy has prompted many Democrats to question Perry’s qualifications for the position. While he governed a state rich in fossil fuels and wind energy, Perry has far less experience than President Obama’s two energy secretaries, both physicists, in the department’s primary work, such as tending the nuclear-weapons stockpile, handling nuclear waste and carrying out advanced scientific research. That’s not to mention, of course, that Perry four years ago called for doing away with the entire department.
However, there’s one realm in which Perry will have plenty of preparation: doling out taxpayer money in the form of government grants to the energy industry.
What often gets lost in all the talk of the Texas job boom under Perry is how much economic development strategy was driven by direct subsidies to employers who promised to relocate to the state or create jobs there. Of course, many states have for years engaged in the game of luring companies with tax incentives. But by the count of a 2012 New York Times investigation, Texas under Perry vaulted to the top, giving out $19 billion in incentives per year, more than any other state.
Perry’s economic development largesse came in many forms, but among the most high-profile were two big pots of money that he created while in office. In 2003, he founded the Texas Enterprise Fund, which he pitched as a way to help him close the deal in bidding wars for large employers thinking of moving to the state. Over the course of Perry’s tenure, which ended in early 2015, the fund gave out more than $500 million. In 2005, Perry created the Emerging Technology Fund, which was intended for start-ups. It gave out $400 million before being shuttered last year by his Republican successor, Greg Abbott.
Disbursements from both funds were controlled by Perry, the lieutenant governor and the speaker of the House. The technology fund had a 17-member advisory board, all appointed by Perry. With such scant oversight, it did not take long for political favoritism and cronyism to creep into the programs. In 2010, the Texas Observer reported that 20 of the 55 Enterprise Fund grant recipients up to that point had contributed directly to Perry’s campaign or the Republican Governor’s Association, of which he became chairman in 2010. Also in 2010, the The Dallas Morning News reported that some $16 million from the Emerging Technology Fund had gone to firms backed by major donors to Perry. For instance, after Joe Sanderson received a $500,000 Enterprise Fund grant to build a poultry plant in Waco in 2006, he gave Perry $25,000. And the Emerging Technology Fund gave $4.75 million to two firms backed by James Leininger, a hospital-bed manufacturer and school-voucher proponent who had helped arrange a last-minute $1.1 million loan to Perry in his successful 1998 run for lieutenant governor and contributed $239,000 to his campaigns over the ensuing decade.
In theory, companies receiving Enterprise Fund grants were accountable for their job-creation pledges and had to make refunds when they fell short. In practice, the numbers proved hard to quantify and few companies had to make refunds. The watchdog group Texans for Public Justice determined that by the end of 2010, companies had created barely more than a third of the jobs promised, even with Perry’s administration having lowered the standard for counting jobs. And in 2014, the state auditor found that $222 million had been given out to companies that hadn’t even formally applied for funds or made concrete promises for job creation. “The final word on the funds is that they were first and foremost political, to allow [Perry] to stand in front of a podium and say that he was bringing jobs back to Texas,” said Craig McDonald, the director of Texans for Public Justice. “From the very start those funds lacked transparency and accountability.”
This being Texas, it was not surprising that many of the leading beneficiaries of the taxpayer funds were in the energy industry. Citgo got $5 million from the Enterprise Fund when it moved to the state from Tulsa in 2004, even though it made clear that it had strategic reasons to move there regardless of the incentive. Chevron got $12 million in 2013 after agreeing to build a 50-story office tower in downtown Houston — a building that three years later remained unbuilt.
Most revealing of the problems associated with the Perry model of taxpayer-funded economic development, though, may have been a $30 million grant in 2004 to a lesser-known outfit called the Texas Energy Center. The center was created in 2003 to be a public-private consortium for research and innovation in so-called clean-coal technology, deep-sea drilling, and other areas. Not coincidentally, it was located in the suburban Houston district of Rep. Tom DeLay, the powerful House Republican, who, it was envisioned, would steer billions in federal funding to the center, with the help of Washington lobbyists hired by the Perry administration, including DeLay’s former chief of staff, Drew Maloney.
But the federal windfall didn’t come through, and the Enterprise Fund grant was cut to $3.6 million, which was to be used as incentives for energy firms in the area. Perry made the award official with a 2004 visit to the Sugar Land office of the Greater Fort Bend Economic Development Council, one of the consortium’s members, housed inside the glass tower of the Fluor Corporation. In 2013, when I visited Sugar Land for an article on Perry’s economic development approach, his administration still listed the Texas Energy Center as a going concern that had nearly reached its target of 1,500 jobs and resulted in $20 million in capital investment.
There was just one problem: There was no Texas Energy Center to be found. Here, from the 2013 article in The New Republic, is what I discovered:
The address listed on its tax forms is the address of the Fort Bend Economic Development Council, inside the Fluor tower. I arrived there late one Friday morning and asked for the Texas Energy Center. The secretary said: “Oh, it’s not here. It’s across the street. But there’s nothing there now. Jeff handles it here.” Jeff Wiley, the council’s president, would be out playing golf the rest of the day, she said. I went to the building across the street and asked for directions from an aide in the office of DeLay’s successor, which happened to be in the same building. She had not heard of the Texas Energy Center. But then I found its former haunt, a small vacant office space upstairs with a sign on an interior wall — the only mark of the center’s brief existence.Later, I got Wiley on the phone. There has never been any $20 million investment, he said. The center survives only on paper, sustained by Wiley, who, for a cut of the $3.6 million, has filed the center’s tax forms and kept a tally of the jobs that have been “created” by the state’s money at local energy companies. I asked him how this worked — how, for instance, was the Texas Energy Center responsible for the 600 jobs attributed to EMS Pipeline Services, a company spun off from the rubble of Enron? Wiley said he would have to check the paperwork to see what had been reported to the state. He called back and said that the man who helped launch EMS had been one of the few people originally on staff at the Texas Energy Center, which Wiley said justified claiming the 600 jobs for the barely existing center.In at least one instance, this charade went too far: In 2006, a Sugar Land city official protested to Wiley that, while it was one thing to quietly claim the job totals from a Bechtel venture in town, it was not “appropriate or honest” to assert in a press release that the Texas Energy Center had played a role. “There is a clear difference between qualifying jobs to meet the [Energy Center’s] contractual requirement with the state and actively seeking to create a perception of [it] as an active, successful, going concern,” wrote the official, according to Fort Bend Now, a local news website. In this case, reality prevailed, and Wiley declined to count the Bechtel jobs.
Today, the $20 million in capital investment from the Texas Energy Center has vanished from the state’s official accounting of Enterprise Fund impact, but the 1,500 jobs remain, part of the nearly 70,000 jobs that the state claims the fund has generated.
Drew Maloney, the former DeLay chief of staff who lobbied for federal funds for the Texas Energy Center, is now the vice president of government and external affairs at the energy giant Hess Corporation.
And Perry is on the verge of being put in charge of vastly larger sums of taxpayer dollars to disburse across the energy industry. (Requests for comment from the Trump transition team went unanswered, as did a request to Jeff Miller, an unofficial Perry spokesman who now works for Ryan, a Dallas-based tax consultancy that helps clients, including ExxonMobil, get tax incentives from Texas and other states.) The Department of Energy has a budget of around $30 billion, oversees a $4.5 billion loan guarantee program for energy companies, and distributes more than $5 billion in discretionary funds for clean-energy research and development. (The loan guarantee program was the source of the $535 million loan that solar-panel maker Solyndra defaulted on in 2011, but it has had plenty of successes as well.) Many of the department’s programs have well-established standards for disbursement, but as secretary, Perry would have a say over at least some of the flow of dollars.
Trump himself, in announcing his nomination of Perry, said he hoped Perry would bring his Texas strategies on energy and economic development to Washington. “As the Governor of Texas, Rick Perry created a business climate that produced millions of new jobs and lower energy prices in his state,” Trump said, “and he will bring that same approach to our entire country as secretary of energy.”
ProPublica is a Pulitzer Prize-winning investigative newsroom. Sign up for their newsletter.