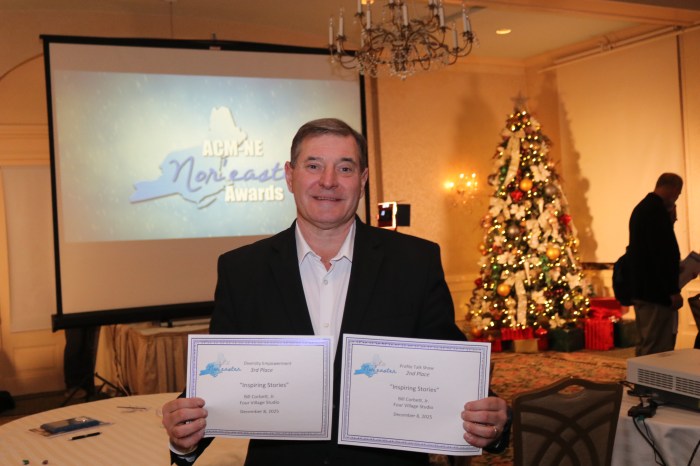
Water Quality Report Card For Manhasset Bay
Tucked between two peninsulas, Manhasset Bay is a beautiful body of water. However, all is not well in Manhasset Bay. As with much of Long Island, the health of this picturesque waterbody is under threat. Save the Sound, an organization that monitors the quality of water in Long Island Sound and its watersheds, gave the Bay an average grade of C for 2023.
Close to shore, the water is subject to human pollutants like nitrogen and stormwater discharge. Nitrogen is an important element of the chemical balance in healthy waterbodies. When the nitrogen levels exceed that normal balance, it throws off all of the other elements, including dissolved oxygen and chlorophyll, leading to a potentially toxic situation. Chlorophyll is related to phytoplankton, which is small algae that float in the water. These phytoplankton are critical for a healthy ecosystem. However, excess chlorophyll, which indicates large blooms of algae in the water, is closely linked to the presence of nitrogen. Excess nitrogen can lead to algal blooms, which are harmful to wildlife and people, and these algae blooms are related to a lower dissolved oxygen level.
Changing how we manage waste water, using an organic fertilizer less frequently, if at all, and slowing and reducing stormwater runoff are all accessible, easy ways to impact water quality in the bay for the better.
Carbon Neutral Nassau By 2035
With rising sea levels and stronger, more frequent extreme weather events, Long Island is on the front lines of climate change. According to the most recent report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) states that greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities are responsible for accelerating global warming and climate change. Higher temperatures, more frequent precipitation and storms, faster rates of ocean warming, and sea level rise are some of the key physical effects of climate change that are impacting communities and ecosystems around the world. Climate change impacts will continue to worsen as global temperatures and greenhouse gas emissions increase.
New York State has already enacted legislation to combat climate change. On July 18, 2019, the Climate Leadership and Community Protection Act (Climate Act) was signed into law. This is among the most ambitious climate laws in the nation and requires New York to reduce economy-wide greenhouse gas emissions 40 percent by 2030 and no less than 85 percent by 2050.
Smoke Impacts
From June 6 to 9, large swaths of the U.S. East Coast were blanketed in wildfire smoke originating in Eastern Canada, where climate change and related environmental factors (e.g. longer summers, shorter winters, less rain, and invasive bark-boring beetles, to name a few) have led to wildfires of increasing intensity and scope in recent years.
Seeing a red sun blotted out in a sky full of woodsmoke is not an uncommon occurrence on the West Coast of North America, where worsening wildfires have ravaged large parts of California, Oregon, Washington, and British Columbia in the past decade.
Here on the East Coast, however, the sight was shocking to many, as was the pervasive smell of woodsmoke and the irritation of particulate matter in our regional air. As a result, perhaps, reactions to the conditions were mixed and somewhat staggered among state and municipal authorities.
School districts and municipalities in lower New York State were mostly left to make their own decisions about the smoke, which is generally a difficult condition to predict, and moved into our area quickly on June 6 after weeks of ongoing fires in Canada.